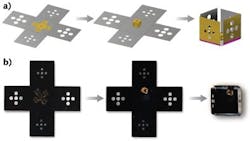
Origami inspires low-power, laser-actuated microstructure folding
Useful photonic components inspired by origami, such as space-based solar panels and telescope mirrors that unfold once reaching orbit, are not new. In contrast to light-actuated folding research from North Carolina State University (Raleigh, NC), researchers from Johns Hopkins University (Baltimore, MD) and the US Army Research Laboratory (Adelphi, MD) have taken the origami concept a step further: They developed a methodology to trigger the folding process for microstructures from afar using low-power handheld lasers.
The process essentially consists of a laser-actuated hinge that folds upon illumination by a compact, inexpensive source such as a 532 nm green laser pointer. A pre-stressed metallic bilayer of chromium-over-gold covered with a heat-activated polymer is patterned between unstressed rigid microstructure segments 300 μm to 3 mm long. The polymer-topped hinges are sequentially illuminated by the laser to begin the folding process, where a two-dimensional (2D), flat, lithographically patterned object is converted into a 3D microstructure. Laser actuation depends on laser wavelength, intensity, and focus; the microstructures can be folded from distances of up to 3 ft and, remarkably, panels can be folded in time periods as short as 67 ms. Contact David Gracias at [email protected].

Gail Overton | Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.