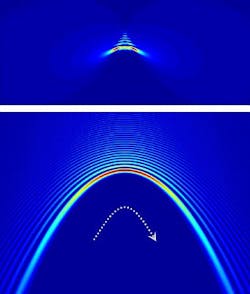
Despite the unique nondiffracting, self-bending, and self-healing properties of Airy beams, these beams are subject to the paraxial limit; that is, Airy beams accelerate along parabolic trajectories and at the limit obey the paraxial wave equation. Because this prevents Airy beams from self-bending into large angles, researchers at the University of California–Berkeley, Lawrence Berkeley National Laboratory, Institut National de la Recherche Scientifique (Varennes, QC, Canada), San Francisco State University, and Nankai University (Tianjin, China) have extended their research and demonstrated that nonparaxial Mathieu and Weber accelerating beams are exact solutions of the Helmholtz equation and can spatially accelerate into large angles along elliptical and parabolic trajectories well beyond the paraxial limit but still retain nondiffracting and self-healing capabilities.1
Using a 532 nm laser source and holographic masks configured with the required phase and intensity information, the researchers experimentally demonstrated both Mathieu and Weber beams in free space; in fact, Airy beams are just special cases of Weber beams at the paraxial limit. Consequently, Weber beams can entirely replace Airy beams for applications as diverse as creating longer plasma channels in air, on-chip routing of surface plasmons around obstacles, and precisely guiding microparticles from one location to another along a preconfigured path. Contact Xiang Zhang at [email protected].
REFERENCE
1. Peng Zhang et al., Phys. Rev. Lett. online; http://prl.aps.org/abstract/PRL/v109/i19/e193901 (November 7, 2012).
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.