Panasonic unveils high-output laser diode for headlights and other uses
As noted in Tech-On!, Panasonic has developed a 405-nm-emitting (blue-violet) semiconductor laser with a high optical output of 4.5 W for use in automotive lights, industrial lighting equipment, and other high-optical-power applications.
The continuous-wave (CW) laser diode can emit at its maximum 4.5 W up to a temperature of 60°C. The output is 50% higher than that of Panasonic's previous 3 W device. Its wall-plug efficiency (the ratio of optical output to input power) is 33%. The company aims to commercialize the device in 2019.
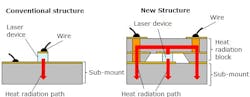
To increase optical output, Panasonic created a heat radiation path on each of the upper and lower surfaces of the laser device; the company's previous product has a heat radiation path only on the lower surface. As a result, heat is radiated from both of the surfaces, lowering thermal resistance from 10.5 K/W to 6.6 K/W.
In addition, Panasonic used aluminum nitride (AlN) for the "heat radiation block" (the heat radiation path on the upper surface). AlN has a high thermal conductivity, and the difference between its thermal-expansion coefficient and that of the GaN-based semiconductor used to form the laser itself is small, making it easier to control thermal stress. (If this difference were large, a large distortion would be produced by the temperature change occurring when operating the laser, potentially causing crystal defects on the laser device.
However, AlN has the disadvantage of high electrical resistance—which Panasonic solved by forming via holes into the AlN.
Source: http://techon.nikkeibp.co.jp/atclen/news_en/15mk/093000066/
About the Author
John Wallace
Senior Technical Editor (1998-2022)
John Wallace was with Laser Focus World for nearly 25 years, retiring in late June 2022. He obtained a bachelor's degree in mechanical engineering and physics at Rutgers University and a master's in optical engineering at the University of Rochester. Before becoming an editor, John worked as an engineer at RCA, Exxon, Eastman Kodak, and GCA Corporation.