LASER DISPLAYS: Liquid-crystal laser promises low-fabrication-cost display
Laser televisions and projection displays have focused on the development of low-cost, high-power red, green, and blue (RGB) laser sources. However, such displays have relatively high cost–associated not only with the lasers, but also with the optics and mechanical assemblies that need to accompany the complex and bulky RGB light engine. In a different approach, researchers at the University of Cambridge (Cambridge, England) have developed a laser display that uses a single laser source to illuminate a liquid-crystal array that can be designed to simultaneously emit RGB color.1 This liquid-crystal laser array dramatically reduces both material and fabrication expenses, potentially enabling a truly low-cost laser display.
A liquid-crystal laser has many advantages over discrete semiconductor lasers. First, any wavelength can be chosen for the output by simply adjusting the photonic bandgap of the liquid-crystal array material. Also, speckle can be reduced by using a short-wavelength laser source or by adjusting the liquid-crystal material to create a broader linewidth for the output illumination. Finally, only one laser source is needed for the liquid-crystal laser display, reducing system cost and complexity.
The first step in demonstrating the liquid-crystal laser display was to select dye formulations to effect RGB lasing from a single-wavelength source. Three dye-doped chiral nematic mixtures were first prepared for operation at 25°C that resulted in bandgaps with long-wavelength edges at 610 (red), 530 (green), and 470 nm (blue). These red, green, and blue chiral mixtures were then capillary filled into separate glass cells consisting of two 1.1-mm-thick pieces of glass rubbed with polyimide alignment layers separated by 10 µm glass beads and glued together to form a 10 × 10 mm cell.
Construction like ordinary LCD cells
These cells use exactly the same construction as typical liquid-crystal displays (LCDs) with edge sealants to contain the fluid liquid-crystal layer. Each cell can be subdivided into three parallel channels (or strips) separated by polymer walls to contain the individual RGB chiral mixtures. The RGB outputs may be combined in the far field to give a white-light output or any combination of colors or wavelengths.
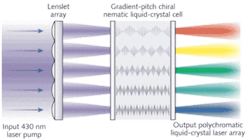
A solid-state laser and an optical parametric oscillator (OPO) completed the 430 nm pump source, with 2 Hz repetition rate, 5 ns pulse width, and delivering up to 40 µJ per pulse. The pump source was then distributed into 100 separate points of illumination using a 10 × 10 lenslet array with a 1.015 mm lens pitch and a 28 mm radius of curvature. Both imaging optics and a spectrometer were used to analyze the output from the liquid-crystal laser (see figure).
When illuminated at 430 nm by the pump source, the RGB liquid-crystal cell produces monochromatic laser emission at 617, 534, and 470 nm, depending on whether the cell contains the red, green, or blue chiral formulation. If the source illuminates a gradient cell that contains two or more liquid-crystal dye formulations, a variety of lasing colors can be observed at the output. Such gradient cells can be readily fixed as soft gels using cross-linkable polymers.
To create a laser display using this technique is then relatively straightforward using standard LCD addressing techniques, says Harry Coles, director of the Centre of Molecular Materials for Photonics and Electronics (CMMPE) at Cambridge University.2 “Each spot can be addressed at will with a very low voltage to be ‘on’ or ‘off,’ thus creating a multicolor laser image,” he explains. “This really is where LCD and laser technology meet. Each spot is a ‘laser’ pixel or conversely each pixel is a laser.”
Coles adds that the application space of this technology is potentially enormous, ranging from combinatorial chemistry, in which two-dimensional arrays of chemical species can be spectroscopically analyzed, to mobile telephones, in which one can envisage the laser array being used to produce images either on screen or by projection. “Indeed, by using suitable projection, a pixel-free display can be produced on a single large-area cell,” adds Coles.
REFERENCES
- Stephen M. Morris et al., Optics Express 16(23) p. 18827 (Nov. 10, 2008).
- www-g.eng.cam.ac.uk/cosmos/
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.