Compact 12 W Q-switched Yb:KGW laser aims at micromachining
Researchers at the Belarusian National Technical University (Minsk, Belarus) and the Nikolaev Institute for Inorganic Chemistry (Novosibirsk, Russia) have created a compact diode-pumped actively Q-switched laser based on ytterbium-doped potassium gadolinium
tungstate (Yb:KGW) gain material. This material enabled a 12.2 W average output power at a 50 kHz pulse-repetition frequency (PRF) and pulse durations of 10 to 24 ns; an optical-to-optical efficiency of 50% was achieved. The high-quality beam had an M2 of 1.2 for all pump powers.
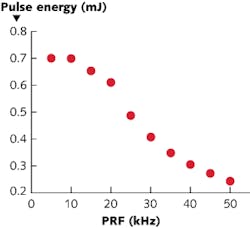
Lasers based on Yb3+ doping are three-level lasers having low stimulated-emission spectra, leading to high pump and intracavity beam intensities, a disadvantage counteracted by having a high PRF and low individual pulse energy. These lasers have the advantage that they can be pumped with commonly available indium gallium arsenide (InGaAs) laser diodes. The researchers first built a continuous-wave (CW) version of the laser that emitted a maximum of 13.6 W, allowing them to estimate the thermal-lens focal length for various pump intensities. The subsequent pulsed version achieved Q-switching through use of a thin-film polarizer and beta barium borate (BBO)-based electro-optical Q-switch in one arm of the cavity. The laser output was linearly polarized; the highest pulse peak power of 70 kW was obtained in the 5 to 10 kHz PRF range. Contact Viktor E. Kisel at [email protected].