High-power direct diode lasers have advantages for heat processing
NORIKAZU KUME
In recent years, fiber lasers and high-power direct-diode lasers (DDLs) have been increasingly used for heat processing. These laser types both have excellent features, allowing them to substitute for conventional lasers in materials processing. Enshu offers these lasers in comprehensive systems for applied technology, processing technology, and peripheral devices.
Processing lasers
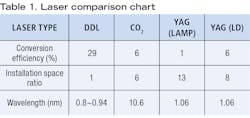
As shown in TABLE 1, the energy-saving advantage of high-power DDLs is clear when compared to conventional types such as carbon dioxide (CO2) lasers and yttrium aluminum garnet (YAG) lasers. Enshu provides laser oscillation units up to 5 kW output based on Japan-made high-power DDLs.Since Enshu’s founding in 2002, the company has been collaborating with Hamamatsu Photonics KK. With this background, Enshu has been developing and manufacturing laser processing machines centered on high-power direct-diode lasers. The company has made an effort to expand Japan-made DDLs in the market by proposing to each customer the practical uses of the advantages of fiber lasers and Japan-made high-power DDLs. Now, the company mainly promotes processing applications that it has developed for these lasers.
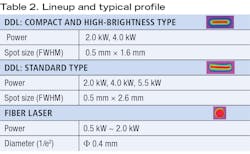
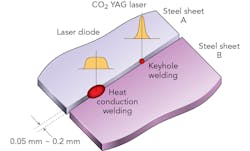
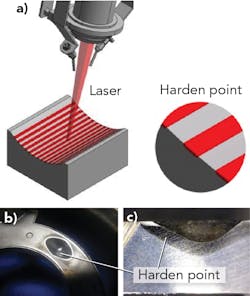
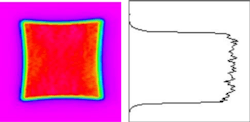
Enshu has now introduced a DDL with peripheral equipment. As seen in FIGURE 1, DDLs are very small. The company also designs and manufactures power supplies and chillers, and can deliver a complete laser unit to customers. This DDL is compact and weighs only 15 kg at 4 kW output, allowing easy mounting on conventional robots and machines. There is almost no loss in the optical system because it is a direct irradiation type.In addition, fiber cable is not used, as the wiring around the head comes from power lines, signal lines, and a cooling water line to simplify wiring and piping work for motion drive devices. The DDL has a rectangular beam spot with a top-hat profile, which allows for heat-conduction welding, a large gap tolerance, and reduced weld spatters (FIGURE 2).
Welding applications
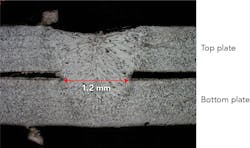
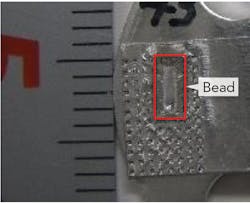
Welding of auto exhaust systems. Auto exhaust parts are produced by lap welding sheet metal. While through-bonding is generally used for lap welding, for exhaust systems, it is necessary to firmly bond the welded part. It is also necessary to prevent the entry of substances such as spatters in the lower area of the bottom sheet. For these reasons, a DDL having a wide bead width and the ability to do conduction welding was adopted. It can be seen in FIGURE 3 that a wide bonding width is obtained and a nonpenetrating weld produced on the lower surface portion.Hardening applications
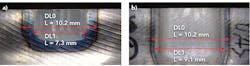
Laser hardening. A DDL can be used to harden a surface. Here, it is not necessary to use an energy absorber because the wavelength is shorter than that of conventional CO2 lasers. Because the beam is a top hat, it is possible to apply heat evenly to the target site without using special optics.Enshu has introduced a new optical lens unit (FIGURE 7) that improves hardening quality by improving the uniformity of the beam, yielding a DDL with uniform illumination unit. The system is offered in 20 different beam sizes needed for heat treatment from 2.5 to 25 mm. The beam size can be selected according to the range. In mass production, the use of a large selection of lenses is considered unnecessary—by narrowing down the types, the initial cost is reduced and the process is simplified. Even with the current type of optical system, an improvement of 11% in hardening width and 11% in hardening depth is realized.
Characteristics of laser cladding
Because conventional cladding technology requires a large amount of heat, distortion of the base material is large and postprocessing is required due to the large amount of residual heat and the resulting dilution into the base material. In the case of laser cladding,1 the applied heat is small and the distortion of the base material is small, making postprocessing unnecessary. In addition, the dilution of alloy into the base material is small, permitting the creation of a high-quality clad layer (FIGURE 8). Also, since the joint between the cladding layer and the base material is a metallurgical bond, it has sufficient strength.Cladding applications
Wire supply-type cladding. A sample of DDL beam cladding is shown in FIGURE 9. In wire supply-type cladding, Enshu mainly works on mold repair and laminated cladding. The DDL is the heat conduction type, so there is less spatter, and the heat transfer is quiet and stable processing can be realized.Powder supply-type cladding. With respect to powder supply-type cladding, Enshu mainly works on wear-resistant parts and mold repair processing. Using this cladding method, the base material for transportation-equipment parts is produced from cheap and light material, rather than select expensive material. Cladding is applied only to an area of a part necessary to satisfy the function, reducing the part cost.
The sample shown in FIGURE 10 resembles a brake disc made from the base material high-carbon steel, which is sometimes surface heat-treated. Producing the disc using low-carbon steel standard, then cladding a high-wear-resistance material onto the disc, produces an inexpensive standard material.Powder supply-type cladding is expected to be effective in improving the construction of future transportation-equipment parts, since the process can use various materials (unlike wire cladding) and can suppress the amount of heat-affected region. Enshu has developed the necessary internally manufactured feeder system for powdered cladding.
Reviewing the DDL technology advantages
To sum up the characteristics of the DDL, the wavelength is shorter than conventional CO2 lasers, so the laser power is easily absorbed by the base material or cladding alloy and can be processed with low power laser output. In addition, the DDL allows for efficient processing without scanning a beam and the beam profile is a top hat, allowing a uniform amount of heat to be applied to the base material.
REFERENCE
1. J. Franks, “High Efficiency Hot Wire Cladding with High Power Diode Laser System,” Industrial Laser Solutions Japan, 1-3.
NORIKAZU KUME ([email protected]) is with the New Business/IOT Promotion Office of Enshu Limited, Minami-ku, Hamamatsu, Shizuoka, Japan; www.enshu.co.jp.