NASA patents dynamically variable spot size laser system
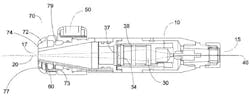
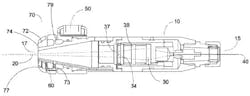
Washington, DC -Workers at NASA have received a US patent for devising a "dynamically variable spot size" (DVSS) system to use in laser welding and laser brazing of metal components. Lasers are a well-accepted method for sensitive welding and brazing operations on small, thin-walled components, accomplishing tight material processing requirements while minimizing heat damage over a reduced spot size. NASA, though, only recently sanctioning their use in very controlled and restricted settings, according to the NASA inventors. The ability to flexibly change the spot size of laser beam is critical depending on the operation being performed, and to accommodating varying sizes of filler metal to be used during brazing processes. (They cite "highly successful" yet underutilized, previous examples of handheld laser systems from Honeywell and GE.) Their new DVSS concept (US #8,290,006) for bonding metal components, about the size of a desktop computer, incorporates "a plurality of lenses" that can be dynamically adjusted to focus and vary the spot size of the laser; spot sizes may range from 0.002-0.075 in. (They cite usage of a 300 W Miyachi-Unitek Nd:YAG fiber-delivered laser). Lens position structural components -- an external pin/rod system, or screws, or an internal movable cam system -- can be dynamically adjusted to vary the spot size of the laser. Each lens may be adjustable or replaceable to provide continuously variable spot size.
The DVSS lens system is designed so that the optimal brazing distance is in a de-focused area of the lens, which allows for a larger spot size for heating the joining area and accommodates varying sizes of filler metal. That optimal working distance can be in a focused area for zoom lens assembly for welding; in some applications, two separate DVSS laser systems may be used for both brazing and welding applications. In some DVSS system embodiments, the system could be positioned at various angles to provide greater positioning flexibility for joining operations. For example, a mirror may be provided at a 45° angle to position the laser beam at a desired work location; the NASA inventors say a mirror may be positioned at any angle required.Here's the full USPTO filing for those who want to dig more into the technical details of the DVSS.