Potomac Photonics' laser micromachining builds micro-fixtures for cardiovascular biomechanics
Halethorpe, MD - At the Center for Cardiovascular Simulation (CCS) at the University of Texas, Austin, Dr. Michael Sacks' group is working with laser micromachining company Potomac Photonics to provide advanced cardiovascular simulations that could enable physicians and biomedical engineers to develop more effective treatments for cardiovascular disease. The specific research aims to simulate the biomechanical function of the cardiovascular system from the continuum-cellular and micro-fibrous tissue to the entire organ level.
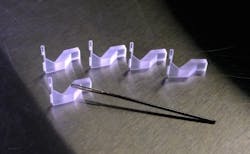
John Lesicko, a member of the CCS research staff, needed to design a micro-scale biaxial testing device. He explains that animal trials would eventually be in mice whose arteries are small so that biaxial testing was required that could handle samples down to 3 × 3mm2.
The new biaxial testing device pushed design limits: 200µm-diameter stainless steel rods were used to pull the material and the individual attachment points needed to be independently actuated without the rods touching each other.
It was clear the tissue attachment elements needed a holder or fixture to make the entire mechanism work properly, but the size needed was very small.
As in most new designs, several modifications of the prototype were required to optimize the configuration so the project was price sensitive. In digital fabrication, such as 3D printing or laser micromachining, all design changes happen in the CAD phase.
It was then inexpensive, quick, and easy for Lesicko to modify the prototype design and try different ideas. He says, "We have now gone through several iterations to find the perfect design and that is priceless!" For example, in the first iteration, the design did not allow enough support for the rods so that they would flex and bend, rather than stay rigid. "Within a week," he says, "we had a design with the necessary support."
With the in vitro modeling in animals, researchers at CCS will be able to test mechanical behavior of the cardiovascular system and then generate population-specific data to give the biotech world accurate models for research. Eventually, the CCS goal is patient-specific modeling that interestingly works hand in hand with the unique mass customization capabilities of 3D printing for direct manufacturing of personalized medical devices. In the meantime, Potomac's 3D printing capabilities are helping CCS prototype new micro-testing devices in order to bring the future possibility of improved treatment to anyone with cardiovascular disease.