Directionally selective light trapping boosts solar-cell efficiency
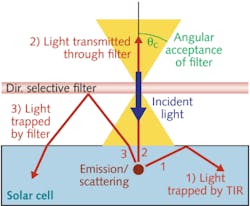
A novel way to trap light in solar cells to boost efficiency is being developed by a team of researchers from the Fraunhofer Institute for Solar Energy Systems ISE (Freiburg, Germany) and IEK5-Photovoltaik, Forschungszentrum Jülich (Jülich, Germany). It is based on an angular transmission characteristic common to many edge-filter optical coatings, in which the transmission of the coating at a certain wavelength drops drastically above a certain angle of incidence and the light is instead reflected. Placed over a solar cell, such a coating transmits sunlight to the cell, but then reflects a large portion of the light scattered from the cell back to the cell.
The researchers fabricated an edge filter with the normal-incidence reflection edge at 1880 nm and placed the filter over a germanium (Ge) solar cell. The filter's reflection band and the cell's spectrally efficient region hardly overlap, so at normal incidence the filter does not much reduce the cell's efficiency. They found that the filter enhanced the cell's absorption of light above 1700 nm, peaking at a 45% increase near the 1900 nm band edge of Ge. The absorption enhancement was due to light trapping and not a suppression of radiative processes. Contact Marius Peters at [email protected].
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.