Researchers Aditya Mohite, Jean-Christophe Blancon, and Wanyi Nie at Los Alamos National Laboratory (LANL; Los Alamos, NM) are studying both the cause and a solution for the tendency of perovskite solar cells to degrade in sunlight. Their research has found both the cause and a solution for this problem, potentially removing one roadblock to commercialization for this promising technology.
RELATED ARTICLE: Make all your photonics from perovskite?
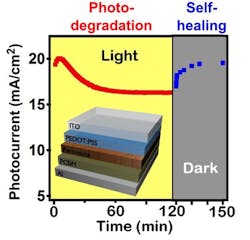
Their paper, "Light-activated photocurrent degradation and self-healing in perovskite solar cells" (DOI: 10.1038/ncomms11574), co-authored by Wanyi Nie and Jean-Christophe Blancon, describes the photo-degradation process. "What we found in this study is that under constant 1-sun illumination the large-grain perovskite solar cells degrade majorly in terms of the photocurrent," Nie said. "But what's interesting is that the devices can self-heal when sitting in the dark for a short while."
The LANL team determined that photo-degradation in perovskite cells is a purely electronic process due to charge accumulation without chemical damage to the crystal structure and therefore can be reduced, while the cells’ self-healing properties allow them to rebound in the dark.
"We can stabilize the device performance by controlling the environmental temperature," said Wanyi Nie, lead researcher on the paper published in Nature Communications. "The degradation of the devices can be suppressed by simply lowering the temperature by few degrees, that is, from 25 degrees Celsius to 0 degrees Celsius."
The team, lead by Aditya Mohite from the Los Alamos "Light to Energy" team in the Material Synthesis and Integrated Devices group, is exploring organometallic halide semiconducting perovskite solar cells. They are promising because of their high power conversion efficiency (PCE) exceeding 20% and the low fabrication costs--the perovskite material is synthesized via a low-temperature solution process. While achieving high PCE is important, the successful transition from a proof-of-concept experiment to actual market-viable photovoltaic technology requires the device to operate with stability under continuous sunlight, of course, and in the air and humidity of outdoor conditions.
By performing extensive device and spectroscopy characterization, the team found that sunlight triggers the activation of meta-stable trap states at relatively low energy deep in the perovskite bandgap, which results in the trapping and captures of photo-generated charge carriers. Over time, trapped carriers can further accumulate in the device, reducing the photocurrent. On the other hand, placing the perovskite solar cell devices in the dark for several minutes allows for "evacuation" of these trapped charges, thus leading to the recovery of the pristine device performances upon the next operation cycle.
"Although several theoretical works have predicted the important role of the organic cation (CH3NH3) in organometallic halide perovskite, it is one of the first joint experimental-theoretical reports on the observation of its impact on the properties of perovskite materials and devices," Blancon said. "Our understanding of the organic cation is still primitive, but our work demonstrates its utmost importance in the photo-stability of perovskite devices and calls for further investigations in the future."
Most importantly this study will provide researchers across the world a first solution to the photo-stability issue in perovskite devices, and future research is now underway toward improvements and the long term technological viability of perovskite-based photovoltaics.
SOURCE: LANL; http://www.lanl.gov/discover/news-release-archive/2016/May/05.17-perovskite-solar-power.php
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.