Microscope detects one million-plus biomarkers for sepsis in 30 minutes
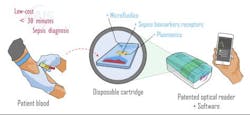
A team of European scientists has invented a microscope that will detect life-threatening infections caused by bacteria such as E. coli and Staphylococcus aureus, and conditions such as meningitis. The microscope, which is about the size of a small book, has the potential to simultaneously detect more than one million biomarkers for sepsis (blood poisoning) at the point of care.
Related: Getting point-of-care devices into the doctor’s office
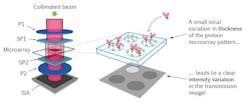
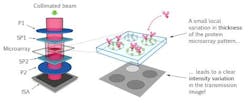
Current tests can take as long as one day to perform—but the new method, which combines photonics technology, microfluidics, and molecular biology, can produce a result in just 30 minutes. By sending polarized beams of light through birefringent crystals and a cartridge containing a blood drop and an array of receptors, the system is able to detect the interaction of light with the bacteria or proteins captured by the receptors. The intensity of the transmission image is then analyzed to provide the physician with an accurate detection of which and how many bacteria or proteins are present.
The microscope was developed by the Scalable Point-of-care and Label-free Microarray Platform for Rapid Detection of Sepsis (RAIS) project, which was coordinated by The Institute of Photonic Sciences (ICFO; Barcelona, Spain). "RAIS can simultaneously examine many biomarkers, such as micro-ribonucleic acids or interleukins, and will let you know the bacteria source much earlier, allowing you to choose the correct treatment sooner," says Dr. Josselin Pello, senior researcher on the project.
With the portable, point-of-care device being easy to use, complete with integrated software, it is thought that not only could this be used in remote areas by junior physicians, but self-diagnosis could be commonplace in the future. A self-diagnosis kit, Pello says, would certainly help with conditions like meningitis, where an early diagnosis could be the difference between life and death.
The RAIS project will conclude at the end of 2017, and has received a grant of over €2.9 million (over $3.2 million) from the EU via the Horizon 2020 and the Photonics Public Private Partnership.
For more information, please visit www.photonics21.org.