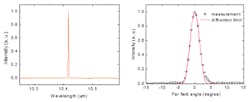
Evanston, IL--Manijeh Razeghi of Northwestern University and her group have once again advanced quantum cascade laser (QCL) technology, this time by creating an angled cavity with a surface-grating-based distributed-feedback (DFB) element that enables a combination of high beam quality (close to pure single lateral mode) with high power. The output of the prototype at a 10.4 um wavelength was more than 6 W, with a nearly diffraction-limited beam quality.
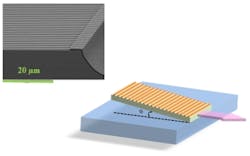
The so-called "beta-DFB" grating is oriented with grating lines parallel with the output laser facet; the laser cavity itself is angled, resulting in a rhomboid cavity shape (see figure).“Our resonator is the most promising device for creating high-power, single-mode laser sources with good beam quality, and it is inexpensive and can be realized at room temperature,” said Razeghi, who heads Northwestern University's Center for Quantum Devices (CQD). “Furthermore, the design can be applied to a wide range of semiconductor lasers at any wavelength.” The development of the beta-DFB is complementary to active research efforts within CQD, but is not yet directly funded.
Refinement of the design, particularly related to optimization of the laser cavity design and improvement of the gain medium, are expected to increase the output power significantly. Applications include standoff sensing to detect gas, explosives, or other materials from a safe distance.
A paper describing the findings, “Angled Cavity Broad Area Quantum Cascade Lasers,” was published August 21 in the journal Applied Physics Letters.
Source: http://www.mccormick.northwestern.edu/news/articles/2012/08/new-approach-for-single-mode-lasers.html