Wavelength-division multiplexing (WDM) passive optical network (PON) architectures typically use passive splitters to increase the number of subscribers in a fiberoptic communications system. But unfortunately, users at the same wavelength still need to compete for time-division multiplexing (TDM) time slots, limiting the overall bandwidth of the system. While active optical switches can allow for dynamic bandwidth allocation, PON enclosures are typically located in cabinets where electrical power is not available, ruling out the use of electrically actuated switches. A solution from Eindhoven University of Technology (Eindhoven, The Netherlands) and Ghent University (Ghent, Belgium) is the development of the first bias-free and optically controlled 1 × 4 switch.
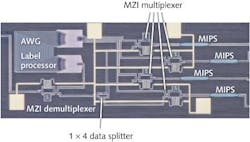
The monolithic switch design is basically a silicon-on-insulator (SOI) integrated circuit comprising passive Mach-Zehnder interferometer (MZI) multiplexers and demultiplexers, and a 200 GHz channel spacing arrayed waveguide grating (AWG) post-processed with four membrane indium phosphide (InP) switches (MIPS) and polymer taper waveguides. Typical on-off extinction ratio of the switch is better than 25 dB at most wavelengths and better than 30 dB in the data-signal range of 1550–1560 nm. For the 1 × 4 switch, error-free operation with a penalty of only 0.8 dB was measured using standard telecom data signals. Contact Oded Raz at [email protected].