Volume 45, Issue 3
Optics
New products
March 1, 2009
Research
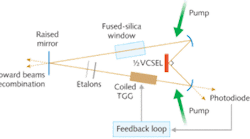
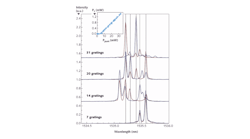
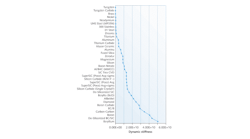
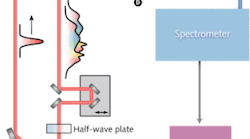
Lasers break new ground
March 1, 2009
Detectors & Imaging
Manufacturers’ Product Showcase
March 1, 2009
More content from Volume 45, Issue 3
More content from Volume 45, Issue 3