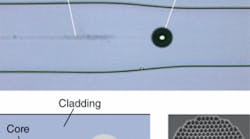
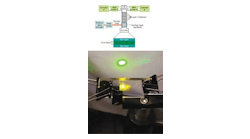
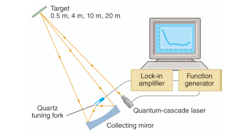
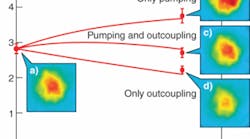
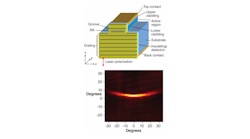
Volume 44, Issue 9
Test & Measurement
New Products
Sept. 1, 2008
Optics
Challenges of change
Sept. 1, 2008
Optics
LASER INDUSTRY REPORT
Sept. 1, 2008
More content from Volume 44, Issue 9
More content from Volume 44, Issue 9
Research
IMAGING & DETECTOR INDUSTRY REPORT
Sept. 1, 2008
Research
FIBER OPTICS INDUSTRY REPORT
Sept. 1, 2008
Optics
OPTICS INDUSTRY REPORT
Sept. 1, 2008