Volume 44, Issue 4
Optics
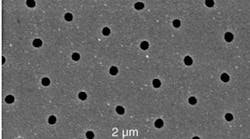
Microspheres simplify nanopatterning processes
April 1, 2008
Optics
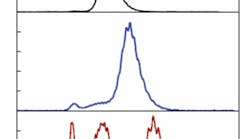
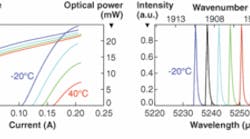
Pump block combines diodes for 350 W output
April 1, 2008
Optics
CMOS photonics breaks through
April 1, 2008
More content from Volume 44, Issue 4
More content from Volume 44, Issue 4