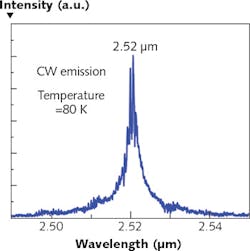
An electrically injected laser diode that relies on a bismuth-containing semiconductor and that emits continuous-wave (CW) in the mid-infrared (mid-IR) at a 2.52 μm wavelength and a temperature of 80 K has been reported by a group of researchers at the Université de Montpellier and CNRS (both in Montpellier, France) and the Paul-Drude-Institut für Festkörperelektronik (Berlin, Germany). The laser can also emit pulsed light at a 2.71 μm wavelength at room temperature.
Grown using molecular-beam epitaxy (MBE), the device is based on gallium arsenide bismuth (GaAs1-xBix) in the form of GaSbBi layers and GaSbBi/GaSb multiple quantum-well (MQW) structures with compositional proportions of GaSb0.885Bi0.115/GaSb. The researchers took great care to optimize the growth conditions to prevent the formation of droplets at the surface of the III-V-Bi epilayers, which would reduce performance. Atomic-force-microscope (AFM) measurements showed a root-mean-squared (RMS) roughness under 0.2 nm. Experimentally, at room temperature, the threshold current density for the 10 × 1160 μm2 area diode was 4.22 kA/cm2 under pulsed operation, while at 80 K, the threshold-current density was 586 A/cm2. The researchers aim to improve the GaSbBi/GaSb MQW structural quality, which will reduce the rather high threshold-current density. Reference: O. Delome et al., Appl. Phys. Lett. (2017); http://dx.doi.org/10.1063/1.4984799.