Light-activated nanoscale heat exchange could create highly efficient energy
Researchers from Columbia Engineering (New York, NY), Cornell, and Stanford have demonstrated, as detailed in Nature Nanotechnology, that heat transfer can be made 100 times stronger than has been predicted simply by bringing two objects extremely close--at nanoscale distances--without touching. Led by Columbia Engineering's Michal Lipson and Stanford Engineering's Shanhui Fan, the team used custom-made ultrahigh-precision micro-mechanical displacement controllers to achieve heat transfer using light at the largest magnitude reported to date between two parallel objects.
RELATED ARTICLE: Quantum dots plus fullerenes create nanoscale photovoltaics
"At separations as small as 40 nanometers, we achieved almost a 100-fold enhancement of heat transfer compared to classical predictions," says Lipson, Eugene Higgins Professor of Electrical Engineering and professor of applied physics. "This is very exciting as it means that light could now become a dominant heat transfer channel between objects that usually exchange heat mostly through conduction or convection. And, while other teams have demonstrated heat transfer using light at the nanoscale before, we are the first to reach performances that could be used for energy applications, such as directly converting heat to electricity using photovoltaic cells."
All objects in our environment exchange heat with their surroundings using light. This includes the light coming at us from the sun, the glowing red color of the heating element inside our toaster ovens, or the "night vision" cameras that enable image recording even in complete darkness. But heat exchange using light is usually very weak compared to what can be achieved by conduction. Radiative heat transfer at nanoscale distances, while theorized, has been especially challenging to achieve because of the difficulty of maintaining large thermal gradients over nanometer-scale distances while avoiding other heat transfer mechanisms like conduction.
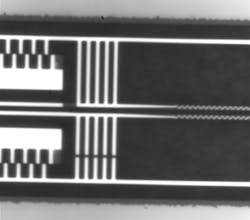
Lipson's team was able to bring objects at different temperatures very close to each other--at distances smaller than 100 nm and demonstrate near-field radiative heat transfer between parallel SiC (silicon carbide) nanobeams in the deep sub-wavelength regime. They used a high-precision micro-electromechanical system (MEMS) to control the distance between the beams and exploited the mechanical stability of nanobeams under high tensile stress to minimize thermal buckling effects, thus keeping control of the nanometer-scale separation even at large thermal gradients.
Using this approach, the team was able to bring two parallel objects at different temperatures to distances as small as 42 nm without touching. In this case they observed that the heat transfer between the objects was close to 100 times stronger that what is predicted by conventional thermal radiation laws (blackbody radiation). They were able to repeat this experiment for temperature differences as high as 260oC (500oF) between the two objects. Such high temperature difference is especially important for energy conversion applications since, in these cases, the conversion efficiency is always proportional to the thermal difference between the hot and the cold objects involved.
St-Gelais and Linxiao Zhu, who co-authored the study and is a PhD candidate in Fan's group at Stanford, note that the team's approach can be scaled up to a larger effective area by simply arraying several nanobeams--on top of a photovoltaic cell, for example--and by individually controlling their out-of-plane displacement using MEMS actuators. The researchers are now looking at applying their same approach for ultra-high-precision displacement control, this time with an actual photovoltaic cell to generate electricity directly from heat.
"This very strong, non-contact, heat transfer channel could be used for controlling the temperature of delicate nano devices that cannot be touched, or for very efficiently converting heat to electricity by radiating large amounts of heat from a hot object to a photovoltaic cell in its extreme proximity," Lipson adds. "And if we can shine a large amount of heat in the form of light from a hot object to a photovoltaic cell, we could potentially create compact modules for direct conversion of heat to electrical power. These modules could be used inside cars, for instance, to convert wasted heat from the combustion engine back to useful electrical power. We could also use them in our homes to generate electricity from alternative energy sources such as biofuels and stored solar energy."
The work received funding from the Defense Advanced Research Projects Agency for award FA8650-14-1-7406 as well as additional support from the Fonds de recherche du Québec--Nature et Technologies (FRQNT) and from the Natural Sciences and Engineering Research Council of Canada (NSERC).
SOURCE: Columbia University/Holly Evarts; http://engineering.columbia.edu/heat-and-light-get-larger-nanoscale
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.