Cambridge, MA--Inspired by nature, materials scientists at Harvard University and the University of Exeter (Exeter, England) have invented a new fiber that changes color when stretched. The researchers identified and replicated the unique structural elements that create the bright iridescent blue color of a hogberry—a tropical plant’s fruit. The multilayered fiber, described in Advanced Materials, could be used in smart fabrics that visibly react to heat or pressure.
The fruit of the South American tropical plant, Margaritaria nobilis, commonly called "bastard hogberry," is low in nutritious content, so mimics a more fleshy and nutritious competitor to make it more attractive to birds that eat the fruit and ultimately release its seeds over a wide geographic area. "The fruit of this bastard hogberry plant was scientifically delightful to pick," says principal investigator Peter Vukusic, associate professor in Natural Photonics at the University of Exeter. "The light-manipulating architecture its surface layer presents, which has evolved to serve a specific biological function, has inspired an extremely useful and interesting technological design."
Vukusic and his collaborators at Harvard studied the structural origin of the seed’s vibrant color. They discovered that the upper cells in the seed’s skin contain a curved, repeating pattern, which creates color through the interference of light waves (a similar mechanism is responsible for the bright colors of soap bubbles.) The team's analysis revealed that multiple layers of cells in the seed coat are each made up of a cylindrically layered architecture with high regularity on the nanoscale. The team replicated the key structural elements of the fruit to create flexible, stretchable and color-changing photonic fibers using an innovative roll-up mechanism perfected in the Harvard laboratories.
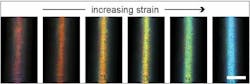
"Our fiber-rolling technique allows the use of a wide range of materials, especially elastic ones, with the color-tuning range exceeding by an order of magnitude anything that has been reported for thermally drawn fibers," says coauthor Joanna Aizenberg, Amy Smith Berylson Professor of Materials Science at Harvard SEAS. The fibers' superior mechanical properties, combined with their demonstrated color brilliance and tunability, make them very versatile. For instance, the fibers can be wound to coat complex shapes. Because the fibers change color under strain, the technology could lend itself to smart sports textiles that change color in areas of muscle tension, or that sense when an object is placed under strain as a result of heat.
This research was supported by the U.S. Air Force Office of Scientific Research Multidisciplinary University Research Initiative, by the UK Engineering and Physical Sciences Research Council, and through a postdoctoral research fellowship from the Alexander von Humboldt Foundation. The researchers also benefited from facilities at the Harvard Center for Nanoscale Systems, which is part of the National Nanotechnology Infrastructure Network supported by the U.S. National Science Foundation. The Wyss Institute for Biologically Inspired Engineering at Harvard also contributed to this research.
SOURCE: Harvard University; http://www.seas.harvard.edu/news-events/press-releases/bioinspired-fibers-change-color-when-stretched
About the Author

Gail Overton
Senior Editor (2004-2020)
Gail has more than 30 years of engineering, marketing, product management, and editorial experience in the photonics and optical communications industry. Before joining the staff at Laser Focus World in 2004, she held many product management and product marketing roles in the fiber-optics industry, most notably at Hughes (El Segundo, CA), GTE Labs (Waltham, MA), Corning (Corning, NY), Photon Kinetics (Beaverton, OR), and Newport Corporation (Irvine, CA). During her marketing career, Gail published articles in WDM Solutions and Sensors magazine and traveled internationally to conduct product and sales training. Gail received her BS degree in physics, with an emphasis in optics, from San Diego State University in San Diego, CA in May 1986.